Relationship Formula
Relationship = Parts/Wholes x Allurement to Communion (Attraction + Creativity + Eros) x Assertion of Autonomy (Repulsion + Destruction + Eros)
Relationships persist in a perpetual state of flux, undergoing continual metamorphosis, and expansion as they traverse the diverse stages of matter, life, human self-awareness, and beyond.
The essence of reality lies in the ongoing evolution of relationships, a dynamic process characterized by a series of transformations toward increasingly profound connections in every conceivable form, spanning across all levels of consciousness and transcending the boundaries of existence.
At its core, reality manifests as the relentless progression of relationships toward deeper depths, unfolding across novel layers of consciousness and intricacy.
Reality itself is synonymous with evolution; it embodies the ceaseless evolution of relationships toward greater profundity, across ever-expanding domains of consciousness and complexity. In essence, reality is the evolution of relationship, and relationship is reality.
Crisis serves as a catalyst for evolution, propelling the ongoing development of relationships toward new levels of coherence and harmony.
Every crisis, regardless of its nature, ultimately stems from a breakdown in relationship.
It is through the resolution of these crises that a new order of relationship emerges, fostering growth, resilience, and adaptation.
Each crisis presents an opportunity for transformation, inviting individuals and communities to transcend existing limitations and forge new pathways toward collective evolution.
In this way, crisis becomes an evolutionary driver, propelling humanity toward greater understanding, cooperation, and interconnectedness.
It is through the evolution of relationships that we navigate the complexities of existence, forging bonds of empathy, compassion, and mutual respect that transcend the limitations of the past and propel us toward a more enlightened future.
Holons
In "A Brief History of Everything," Ken Wilber discusses Arthur Koestler's concept of holons.
Holons are entities that are simultaneously whole and part, possessing both autonomous selfhood and embeddedness within a larger whole.
Koestler introduced this idea in his book "The Ghost in the Machine," suggesting that all entities in the universe can be understood as holons, existing within a hierarchy of wholes and parts.
According to Koestler, holons exhibit two key characteristics: autonomy and dependence.
There is no satisfactory word in our vocabulary to refer to theseJanus-faced entities: to talk ofsub-wholes (or sub-assemblies, sub-structures, sub-skills, sub-systems) is awkward and tedious.
It seems preferable to coin a new term to designate these nodes on the hierarchic tree which behave partly as wholes or wholly as parts, according to the way you look at them.
The term I would propose is 'holon', from the Greek holos = whole, with the suffix on which, as in proton or neutron, suggests a particle or part.
They are autonomous in that they possess a degree of self-organization and agency, capable of interacting with their environment and other holons. However, they are also dependent on the larger whole of which they are a part, influenced by the context in which they exist.
Wilber expands on Koestler's concept of holons in his integral theory, which provides a framework for understanding the interconnectedness of all phenomena in the universe.
In Wilber's view, holons can be found at every level of existence, from subatomic particles to individual organisms to social systems and beyond. Each holon operates according to its own internal dynamics while simultaneously contributing to the larger whole of which it is a part.
Koestler's concept of holons offers a valuable perspective for understanding the complex interplay between autonomy and interdependence in the natural world, shedding light on the fundamental dynamics of evolution and organization across multiple scales of existence.
Works Cited
Publishing Group, Amplify. “First Principles and First Values.” Amplify Publishing Group, amplifypublishinggroup.com/product/nonfiction/politics-and-current-affairs/first-principles-and-first-values/.
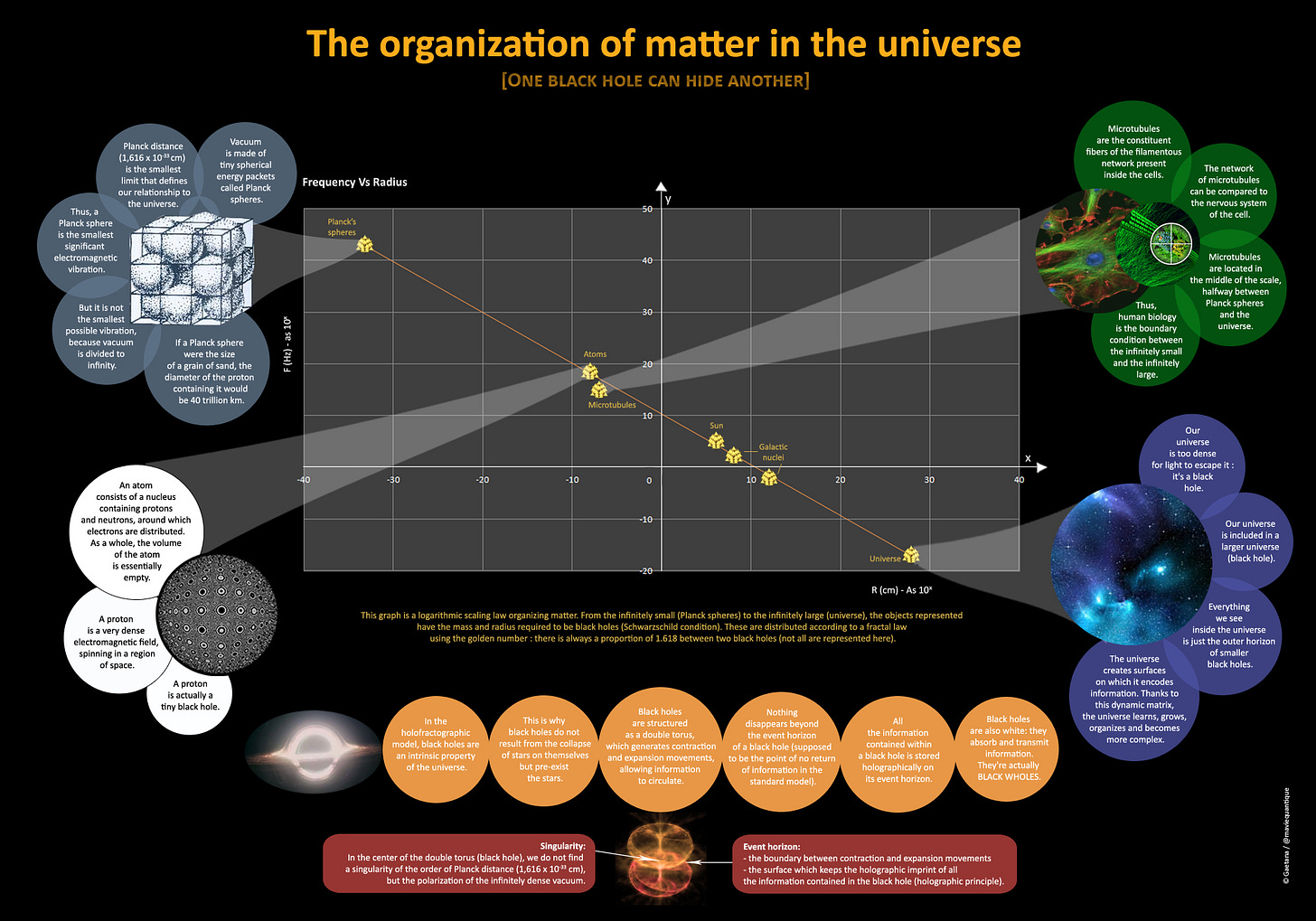
Haramein, Nassim. “HARAMEIN’S SCALING LAW for ALL ORGANIZED MATTER (USR - BLACK HOLES - GALACTIC ENGINES).” Www.youtube.com, www.youtube.com/watch?v=eswomuU8hIE.
Johnson, Christopher. “A SCALING LAW for ORGANIZED MATTER in the UNIVERSE.” Www.academia.edu, www.academia.edu/18718824/A_SCALING_LAW_FOR_ORGANIZED_MATTER_IN_THE_UNIVERSE.
Wilber, Ken. A Brief History of Everything. Shambhala, 2007.
Koestler, Arthur. The Ghost in the Machine. Last Century Media, 2016.
Donate
If this post was supportive and you want to donate, you can to so through the links below:
PayPal Donate (@valuenathan)
Venmo Donate (@Unique_Self_Value)
CashApp Donate ($uniqueselfmoney)
Donate To Me Via Blockchain
Litecoin MKrPai4qLJDuYSJSjxADiKxxiJvY1BXye7
Bitcoin Cash bitcoincash:qzx2qnrh4uvwap6ys9w77nw3eew94hsccy0svrfhyu
Ethereum 0x983480369920eE15520518376cb52b156285dC0a
Bitcoin 3HkFJoxdNr4daMSp1oWepwA2SuJ6Uz3SKm
Dogecoin DAs9EgsQiUSuPazH8Hcpkqu65zg8ypDZzu